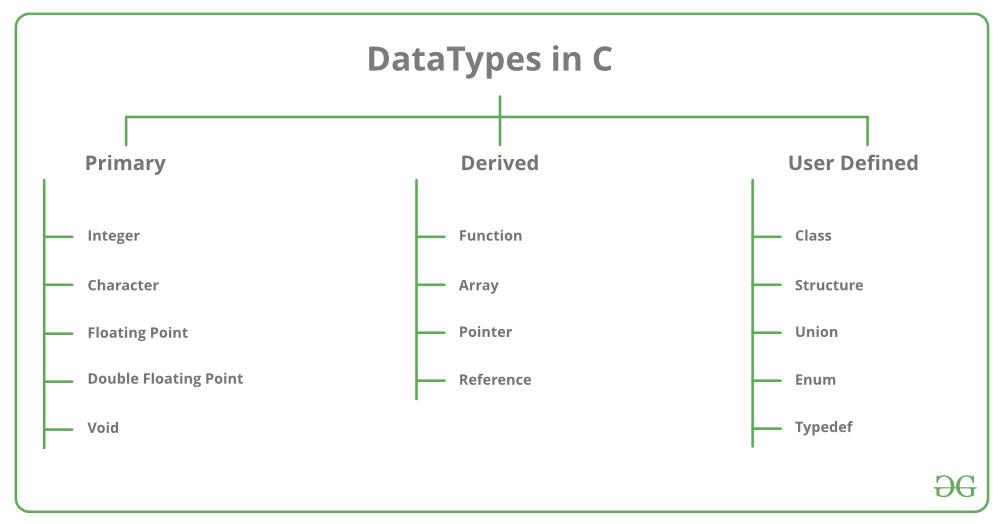
Each variable in C has an associated data type. It specifies the type of data that the variable can store like integer, character, floating, double, etc. Each data type requires different amounts of memory and has some specific operations which can be performed over it. The data type is a collection of data with values having fixed values, meaning as well as its characteristics.
The data types in C can be classified as follows:

Different data types also have different ranges up to which they can store numbers. These ranges may vary from compiler to compiler. Below is a list of ranges along with the memory requirement and format specifiers on the 32-bit GCC compiler .
| Data Type | Size (bytes) | Range | Format Specifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| short int | 2 | -32,768 to 32,767 | %hd |
| unsigned short int | 2 | 0 to 65,535 | %hu |
| unsigned int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 | %u |
| int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | %d |
| long int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | %ld |
| unsigned long int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 | %lu |
| long long int | 8 | -(2^63) to (2^63)-1 | %lld |
| unsigned long long int | 8 | 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 | %llu |
| signed char | 1 | -128 to 127 | %c |
| unsigned char | 1 | 0 to 255 | %c |
| float | 4 | 1.2E-38 to 3.4E+38 | %f |
| double | 8 | 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 | %lf |
| long double | 16 | 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932 | %Lf |
Note: The l ong, short, signed and unsigned are datatype modifier that can be used with some primitive data types to change the size or length of the datatype.
The following are some main primitive data types in C:
The integer datatype in C is used to store the integer numbers(any number including positive, negative and zero without decimal part). Octal values, hexadecimal values, and decimal values can be stored in int data type in C.
We use int keyword to declare the integer variable:
int var_name;The integer data type can also be used as
Note: The size of an integer data type is compiler-dependent. We can use sizeof operator to check the actual size of any data type.